It is estimated that hundreds of different varieties of mold may be found in nature. Some can be good for your health, while others might be dangerous. “Cobweb Mold” is a common name for a sort of mold that you could find in your house. Here we are talking about how to identify Cobweb mold and how to get rid of it easily and safely.
It isn’t simply one mold species in general. It’s more like a collection of closely related mold species that produce cobweb disease in mushrooms. Cobweb mold species are so similar to one another that only thorough genetic testing can tell them apart.
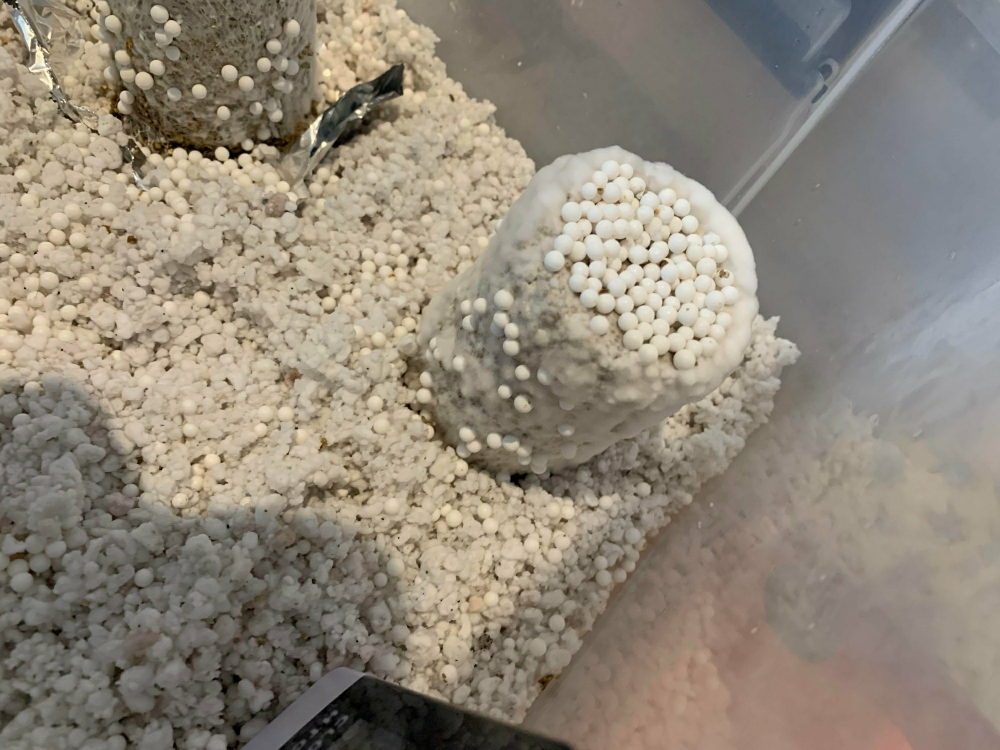

How To Identify Cobweb Mold And Get Rid Of It?
They’ve been reclassified over the years, which has prompted dispute among mycologists worldwide. In the United States, the two species Dactylium and Dactylium Dendroides are most commonly referred to as the causal agents of cobweb mold. Cladobotryum, on the other hand, is more common in eastern nations. Hypomyces or Hypomyces Rosellus are two more species that have been lumped into this category.
You might want to read this: Lasagna Gardening 101: Advanced Guide To Building No-till, No-Dig, Immediate Planting Method
Species:
Mold, fungus, and mushrooms all share one trait. It’s known as the mycelium, which is a fungus’s vegetative or growing body. That may seem difficult to grasp, so let’s take a look at a typical mushroom as an example.

Mycelium of Mushrooms
Many people mistakenly believe that a mushroom is an entire plant; however, this is not true. The mushroom is, in reality, the fruit of mycelium, which develops and flourishes beneath the ground’s surface. When two distinct types of mycelium come together underground, they form a fruiting body, in this example, a mushroom, and that fruit is what you see above ground. The fruiting body disperses spores into the air, which land on the ground and sprout new mycelium.
Mold in the Bathroom Mycelium Mold acts in the same way that mushrooms do. The mycelium seeks gaps and crevices to anchor and grows from, so bathroom tile grout is enticing.
When two mycelium come into contact, precisely like a mushroom, they send up a fruiting body; however, in the case of bathroom mold, these bodies are minuscule. Alternatively, the fruiting bodies, like the mushroom, release spores into the air, which settle in other regions and continue to develop.
Cobweb mold vs mycelium
Cobweb mold and mycelium are often confused, but they are very different things. Cobweb mold is a bad guy that can ruin your mushroom cultivation by eating your crop and causing disease. Mycelium is a good guy that is actually the root-like part of the mushroom that helps it grow and also benefits other plants.
Cobweb mold is gray, whispy, and smelly, while mycelium is white, ropey, and fresh. Cobweb mold grows super fast, while mycelium takes its time. You don’t want cobweb mold in your growth, but you do want mycelium.
Where Is Cobweb Mold Found?
Cobweb mold, also known as Dactylium mildew, is this funky fungus that can show up in different places. It’s like this fuzzy, cobweb-like mold that loves places with lots of moisture and organic stuff. So, you might find it hanging out in both indoor and outdoor spots.
Think of damp areas where air doesn’t flow too well. Basements, attics, and bathrooms are prime spots for cobweb mold to party. It also loves places with stored stuff like cellars, where you stash old books, papers, and cardboard boxes. Oh, and don’t forget greenhouses with their warm and humid conditions. Cobweb mold can’t resist growing on decaying plant matter or hiding in the corners.
You might even spot it invading your houseplants, especially if you’re a little too generous with the watering can. And let’s not forget about agricultural settings, like farms and barns, where hay, straw, and crops create a cozy environment for cobweb mold to thrive.
Now, don’t go panicking! Cobweb mold is usually more of a bother than a serious health threat. But if you have allergies or respiratory issues, exposure to a lot of mold spores could make things uncomfortable. If you suspect you’ve got cobweb mold or any other mold hanging around, it’s a good idea to bring in professionals who know how to deal with it safely.
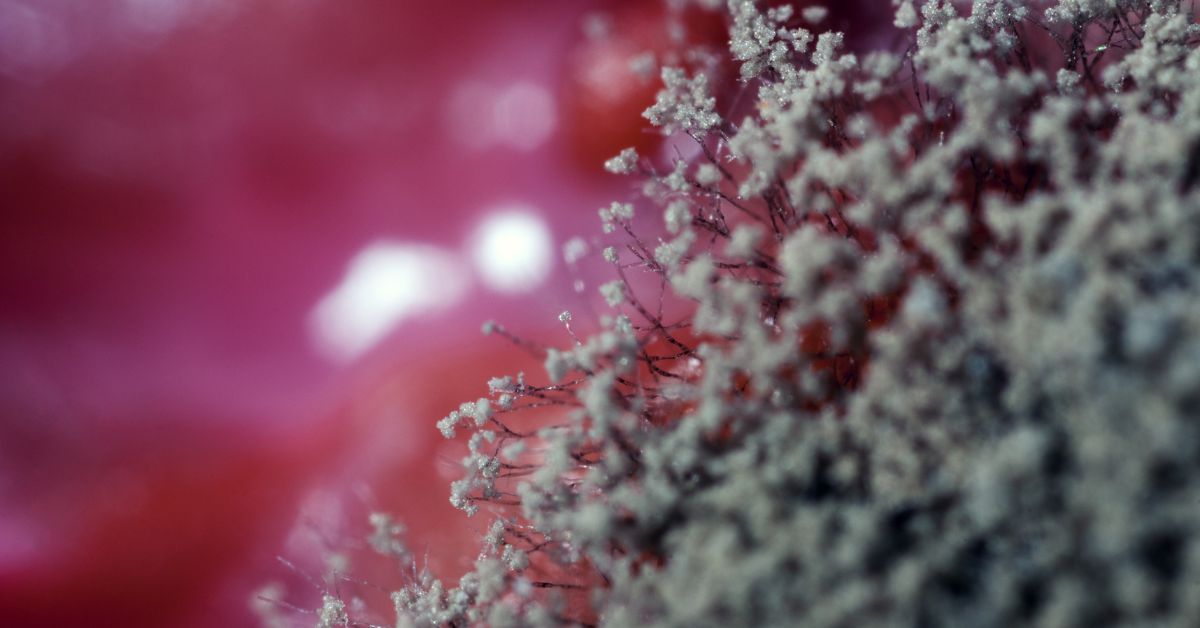
Cobweb mold is most typically observed on the casing layers of mushrooms. This isn’t the only place you’ll find it, though. Cobweb mold may theoretically grow on any uncolonized substrate if a suitable host is present.
Simultaneously, investigations have revealed that adding spores or mycelium pieces to spawn causes cobweb disease in other fungus forms. This shows that various factors might encourage or prevent the growth of cobweb mold.
One thing is certain: once established, cobweb mold has the power to swiftly spread. This property implies it can quickly fragment and grow from one fungal substrate to the surrounding environment. It also implies that a single colony can expand to several locations.
You might want to read this: 7 Health Benefits of Moringa Tea You Never Imagined
You should also keep in mind that the mold’s development rate is directly proportional to its developing conditions. This also means that altering the environment can assist in swiftly dealing with an epidemic. Slowing the growth of cobweb mold can sometimes be as easy as reducing the ambient temperature or changing the RH. It could even be able to stop it totally.
Cobweb mold is most commonly found in later flushes, which is crucial for appropriately recognizing it and finding the source of the contamination. It reproduces by spores, just like the majority of mold species. A little quantity of spore may have been there in the past and was only waiting for the ideal conditions to activate it.
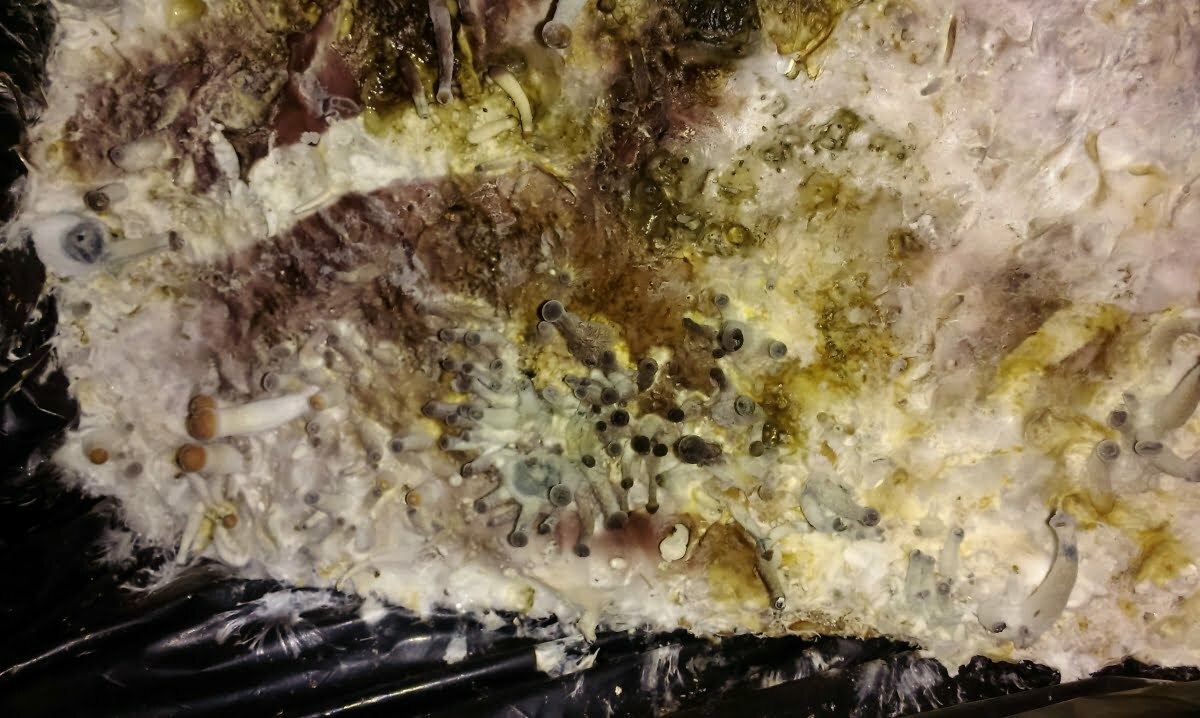

This suggests that the formation of cobweb mold in earlier flushes may have been caused by mycelium fragmentation and that it may be present in another adjacent source. It might be as easy as having rotting fruit in the same room.
Of course, an elder mushroom stump is one of the most typical sources of origin. It’s vital to note that this has very little to do with the stumps decaying. A cobweb mold-infected mushroom might have just left a cobweb mold-infected stump.
Cobweb Mold And Aborts
Aborts are another major source of cobweb mold. This does not necessarily imply that all aborts must be picked up right away. However, whenever you harvest your other mushrooms, you should make a conscious effort to remove all aborts, which can be time-consuming if the batch in question has a large number of aborts.
There’s a lot of leeway regarding how you understand something and, eventually, act on it. There is unquestionably a link between the development of cobweb disease and the presence of aborts. However, it’s difficult to establish if the aborts directly result from the cobweb mold or if the cobweb mold was the root cause of the aborts!
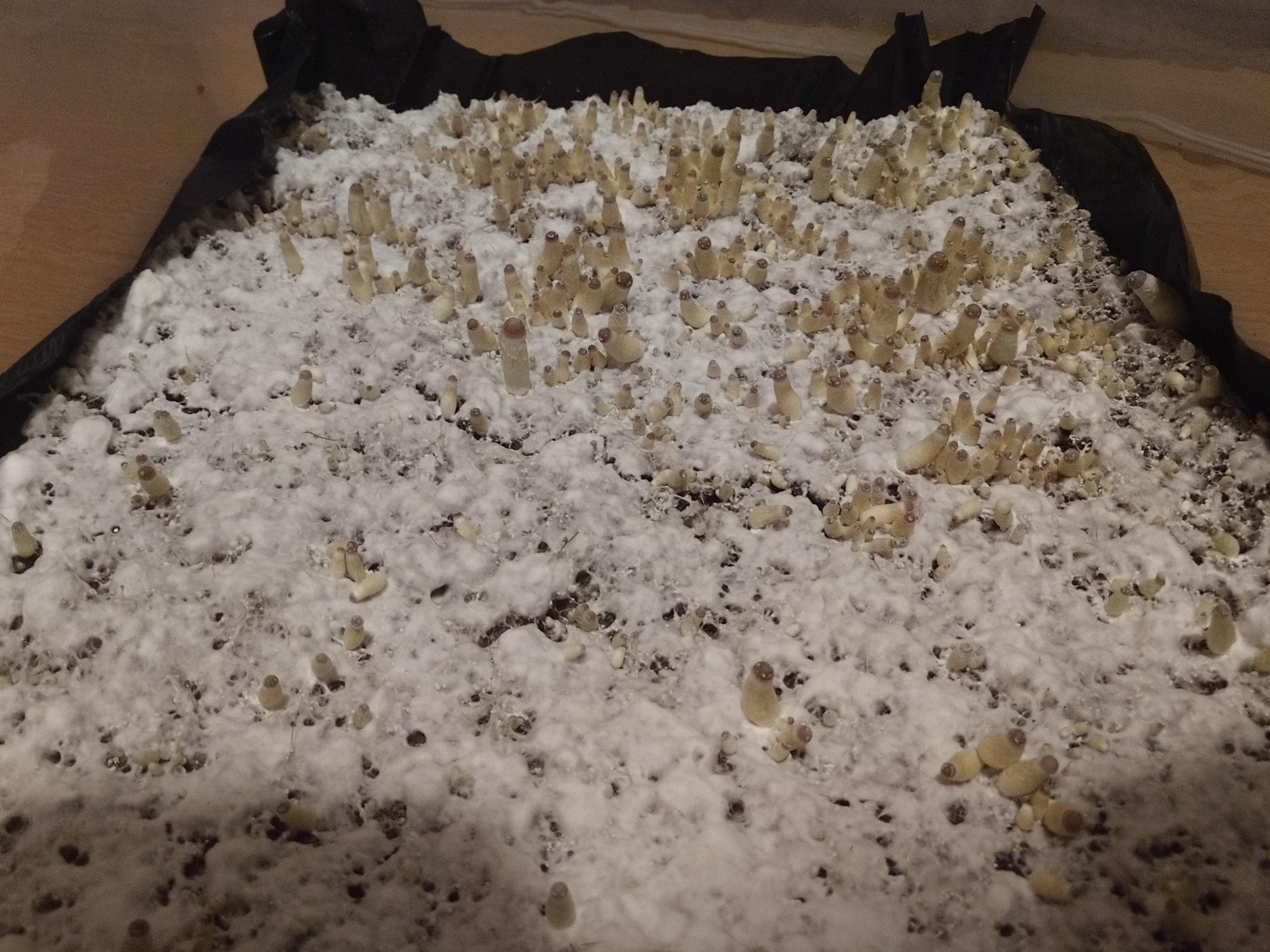

Correctly Identifying Cobweb Mold
It’s also worth remembering that there are other varieties of mold that resemble cobweb mold but aren’t. Many people have misidentified low-density grey mold as cobweb mold. There are additional forms of pinhead mold, which has small black pinheads and is sometimes mistaken for cobweb mold.
Pin molds are more frequent contaminants found in spawn as well as various bulk substrates. Pin molds are more prevalent pollutants found in spawn and other bulk substrates, whereas cobweb mold is more likely to form in the casing layers. The development rate of these molds can match or even exceed the typical growth rate of cobweb molds under ideal conditions.
The other varieties of mold are significantly more difficult to cure, despite their similar appearance. Misidentification contributes to this by giving the impression that actual cobweb mold is difficult to treat.
In actuality, cobweb mold is a simple problem to solve. One widespread myth is that hydrogen peroxide is exclusively effective against cobweb mold. The truth is that this highly oxygenated solution reacts violently with almost every species of fungus, and it can even harm mushroom mycelium!
Treating Cobweb Mold
When hydrogen peroxide is given to fungus, the most frequent reaction is this type of vigorous fizzing. The rapid conversion of h202 into its basic elements, water and oxygen, is the direct cause of this. In semi-controlled settings, looking at the casing surface is the most efficient means of spotting cobweb mold.
This will aid in accurate identification, which is the first step toward successful rehabilitation.
Using salt to get rid of cobweb mold
Salt is an effective natural remedy for combating cobweb mold because it helps to dry out the affected area and create an uninhabitable environment for mold growth. To use salt to get rid of cobweb mold, start by mixing about 1 tablespoon of salt into a quart of water. You can then apply this mixture directly to the affected area using a spray bottle or a cloth.
Be sure to thoroughly soak the affected area with the salt solution, taking care to cover all surfaces where the mold is present. After applying the salt solution, allow it to sit for a few hours before wiping away any excess liquid. You may need to repeat this process a few times over the course of several days until the mold has been completely eliminated.
It’s worth noting that while salt can be effective against cobweb mold, it should be used with caution on plants or other materials that may be sensitive to salt. Additionally, if the mold infestation is severe or persistent, it may be necessary to employ additional strategies, such as increasing ventilation or reducing humidity levels in the growing environment.
You might want to read this: Free Gardening T-Shirt Designs Download For Our Followers: Print Ready SVG, and PNG
How do I get rid of cobweb mold on mycelium?
If cobweb mold disease exists and actively keeps growing (e.g., on mycelium), it is frequently best treated by laying a moist paper towel over the growth to retain any spores that have not yet escaped. After that, sprinkle salt on the paper towel before carefully removing any mushrooms with spotting symptoms.
While this may appear challenging, keep in mind that your ultimate aim is to eradicate the appearance of cobweb mold in the casing layer. Even if there is just minor contamination, many healthy mushrooms may survive and even grow!
How do I know if mycelium is contaminated?
Your culture is most certainly infected if you see green, blue, grey, or black spots on or in your fruiting box. Small blue spots in the mycelium, on the other hand, might represent bruises rather than mold. Some blue patches may appear as the rye rubs the mycelium against the grow box.
How do you deal with cobweb molds?
When cobweb mold illness is present, it is generally best treated by laying a moist paper towel over the growth to retain any spores that have not yet escaped. After that, sprinkle salt on the paper towel before carefully removing any mushrooms that have spotting symptoms.
Is mycelium supposed to look fuzzy?
Mycelium can appear fuzzy, thread-like, or both at once. Although there is a high population of mycelium, you should be able to see the water droplets sitting on the mycelium. … This type of mycelium growth is a good indicator.
Does mold have mycelium?
Molds may grow on decaying organic materials wherever in nature, but their presence is only noticeable to the naked eye when enormous colonies occur. A mold colony is made up of an interconnected network of hyphae termed a mycelium rather than individual organisms. At the hyphal tip, nutrients are absorbed.
How do you get rid of mushroom contamination?
1. Laminar Flow Hood. A laminar flow hood is the greatest way to minimize pollutants in the air.
2. Air Box that is still. A still air box, or SAB, is another method for reducing airborne pollutants. …
3. Sterilization. …
4. Pasteurization. …
5. Use Proper Technique. …
6. Flaming your Scalpel. …
7. Using Alcohol.
What does spider web mold look like?
The thread-like mold resembles a spider web. The mold that is peeping through vinyl-based wallpaper sometimes appears in brighter colors of purple, pink, or orange. Mold growth can be seen, indicating that the mold has spread.
What causes white fuzzy mold on food?
Mold grows from spores floating through the air. When some of these spores land on damp food, mold forms. Food mold survives by creating substances that cause the food to degrade and decompose. At first glance, a common mold that develops on bread seems to be white cottony fluff.
Can bulk substrate get contaminated?
Mycelium will still be able to grow on this substrate despite the presence of these micro creatures. When the bulk substrate is sterilized, it becomes almost as sensitive to pollutants as highly nutritious spawn substrates like rye berries and brown rice.
What are Hyphal knots?
A hyphal knot is the first stage of a mushroom fruit body. This is when the individual hyphae strands form a bundle and prepare to become a mushroom. After that, a little cluster of visible bumps forms on the mycelium’s surface.
How do you get rid of mold?
When warm, humid air meets a surface that is cooler than the surrounding air, condensation can form. When water gathers on porous surfaces, mold may form.
What’s the difference between a fungus and a mold?
Fungi is a kingdom of eukaryotic and heterotrophic creatures with a huge number of species. Molds are fungi that are multicellular microscopic creatures defined by the presence of multicellular filaments known as hyphae.
Why did this happen the grains in the humid air got moldy?
When warm, humid air comes into touch with a surface that is cooler than the surrounding air, condensation can form. When moisture pools on porous surfaces, mold can form.
Is my mushroom moldy?
While some mushrooms develop mold as they rot, one indicator is always a sure sign of poor mushrooms: a slimy film that forms as they become rotten. However, if the mushrooms have become squishy and slimy, they are most certainly past their prime and should not be ingested (via Cooking Light).
What type of mold is mildew?
Mildew refers to mold or fungus of many types. Mildew is a phrase typically used to refer to mold growth with a flat growth tendency. Molds are tiny fungi that develop in the form of hyphae, which are multicellular threads.
What is Tomentose mycelium?
Rhizomorphic growth is usually the result of a healthy mycelium, and it strengthens the mycelium’s grip on the substratum. Tomentose growth, which means ‘of or resembling matted hair,’ is the second form of growth, which is wispier in character. Depending on genetics, it can be just as excellent as or better than rhizomorphic growth.
How do you remove fuzzy mold?
Fill a spray bottle halfway with baking soda and water and shake to dissolve the powder. Scrub the moldy surface with a gentle brush or soft cloth after spraying the solution on it. If the mold needs extra disinfection, sprinkle some baking soda and water solution on it after cleaning. Use distilled vinegar instead of regular vinegar.
What is white fuzzy mold called?
White mold is commonly confused for efflorescence, which is a white, almost fluffy crystalline development. Salt deposits cause it to develop on brick, concrete, and stucco.
How do you pasteurize large amounts of substrates?
Put your straw in a wash bag or pillowcase and soak it in 160°F water for one hour to pasteurize it. This may be done on a modest scale inside on a burner. Use a 55-gallon barrel and a butane burner for greater operations. When the straw is finished, it must be carefully drained.
What are mushroom pins?
Initials are quite minute; however, they may be observed as rhizomorph outgrowths. The structure is known as a “pin” after it quadruples in size. During the button stage, pins continue to spread and get bigger, eventually transforming into a mushroom. After 16 to 18 days, harvestable mushrooms appear.
What does primordia look like?
Primordia are commonly seen as a clump of mycelium threads that eventually form a cap and a characteristic stipe. Hyphal Knots is another name for Primordium…. Cubensis primordium may be observed as white knots/balls of mycelium in this shot. On rhizomorphic mycelium, primordial growth may be detected.
Do hyphal knots turn into primordia?
Mycelium condenses to form hyphal knots, which mature into “primordia,” or young mushrooms.
What kills mold better bleach or vinegar?
Both vinegar and bleach are effective at preventing mold development in the home. Both, however, have advantages and downsides. Vinegar is a better alternative to bleach. If mold forms on porous surfaces, vinegar can penetrate deep into the pores and destroy 82 percent of the mold.
How do you treat mold with vinegar?
Fill a spray bottle halfway with undiluted vinegar. It should be sprayed immediately onto the moldy area. Allow at least an hour for the vinegar to rest. Scrub the moldy surface with a soft bristle brush until the mold is gone.
Is there a spray that kills mold?
Overall winner: RMR-141 Disinfectant and Cleaner by RMR Brands This is an EPA-approved mildew spray, which implies it’s a chemical agent that can prevent mildew from growing. It kills mold, mildew, bacteria, and other germs and has been proved effective against 141 distinct microorganisms.
Is cobweb mold dangerous?
Yes. Cobweb mold is harmful and toxic to living things, especially mushrooms, as it causes a serious disease called cobweb disease. It is unclear whether mushrooms contaminated with cobweb mold are safe to eat, but some growers advise against it. Cobweb mold looks like a gray, fuzzy, web-like material that grows over the substrate and the mushrooms. It also has a mildewy smell. Cobweb mold grows in still, dry, hot, stale air and can be prevented by proper sterilization and ventilation.

How do I mold mycelium?
- Step 1: Gather Supplies. Inoculated Grain Spawn (mycelium) …
- Step 2: Prepare Molds. …
- Step 3: Sterilize and Prepare Your Workspace. …
- Step 4: Sanitize Substrate. …
- Step 5: Combine Substrate & Grain Spawn. …
- Step 6: Fill and Seal Molds. …
- Step 7: Let It Grow. …
- Step 8: Bake & Finish.
How do you remove white mold from wood?
- Shake up a teaspoon of soap in a spray bottle filled with water.
- Spray the damaged area and gently scrub away the mold with a soft-bristled brush, sponging up any leftover liquid as you clean.
- Using a cloth, fully dry the surface.


